How AI Is Revolutionizing Agriculture? , Feeding the Future with Intelligent Farming. By 2050, the global population is expected to reach a staggering 10 billion. How will we sustainably feed this growing number of people while facing limited resources and the increasing challenges of climate change? The answer may lie in the transformative power of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is rapidly changing agriculture, empowering farmers to produce more food with fewer resources and a smaller environmental impact. This article explores how AI in agriculture is reshaping the farming landscape, examining its benefits, applications, challenges, and promising future.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture
AI refers to machines mimicking human intelligence to perform tasks like problem-solving, learning, and decision-making. In agriculture, AI is proving to be a game changer offering solutions to some of the most pressing challenges in the industry
- Labor Shortages: AI-powered automation can handle labor-intensive tasks like weeding, harvesting, and livestock monitoring.
- Resource Scarcity: AI can optimize the use of essential resources like water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Climate Change: AI helps farmers adapt to unpredictable weather by predicting patterns and optimizing irrigation.
- Increasing Food Demand: AI enables data-driven decisions about planting, fertilization, pest control, and animal health to increase crop yields and livestock production.
Evolution of AI in Agriculture
The integration of AI into agriculture has evolved over decades:
- 1980s: Early expert systems provided basic crop management recommendations.
- 2000s: Machine learning algorithms enabled advanced data analysis for soil health and crop performance.
- 2010s: IoT devices revolutionized precision farming with real-time monitoring.

Today: AI integrates robotics, drones, and predictive analytics for smarter farming practices
The Benefits of AI in Agriculture: A New Era of Farming:
Adopting AI technologies in agriculture is leading to a significant shift in farming practices, offering numerous benefits for farmers, consumers, and the environment.
Enhanced Productivity Through AI
- Predictive Analytics for Weather Forecasting: AI algorithms analyze historical weather data, satellite imagery, and real-time sensor data to predict weather patterns with increasing accuracy. This allows farmers to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvesting, minimizing crop damage from extreme weather. For example, AI can predict the likelihood of frost, heavy rainfall, or drought, enabling farmers to take proactive measures to protect their crops.
- Precision Farming for Optimized Resource Allocation: AI-powered precision farming uses sensors, drones, and GPS to create detailed field maps, identifying variations in soil conditions, crop health, and pest infestations. This enables the targeted application of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, optimizing resource use and maximizing yields. Imagine a field where each plant receives exactly the amount of water and nutrients it needs, minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
- Real-Time Monitoring for Improved Crop Health: AI-enabled sensors, drones, and robots continuously monitor crop health, detecting early signs of stress, disease, or pest infestations. This real-time data allows for timely intervention, preventing widespread problems and ensuring healthy growth. This is like having a 24/7 health checkup for your crops, allowing for early detection and treatment of issues.
Cost Savings with AI-Driven Solutions:
- Automated Weeding and Harvesting: AI-powered robots are increasingly used for weeding and harvesting, reducing manual labor and associated costs. These robots can operate for longer hours with greater precision, increasing efficiency and minimizing waste. For instance, robotic weeders can identify and remove weeds without harming crops, reducing the need for herbicides and manual labor.
- Optimized Resource Use: By precisely tailoring the application of resources like water and fertilizers, AI in agriculture helps farmers reduce input costs while also minimizing environmental impact. This is particularly important in regions facing water scarcity or where fertilizer runoff can pollute waterways.
- Reduced Crop Losses: AI helps predict and prevent crop losses by identifying potential threats like pests, diseases, and extreme weather. Early detection and intervention minimize damage and ensure a higher return on investment. For example, AI can analyze weather patterns and historical data to predict the likelihood of a pest infestation, allowing farmers to take preventive measures.
Sustainability and AI in Farming:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: AI is crucial in promoting sustainable agriculture practices. By optimizing resource use and minimizing chemical applications, AI in farming helps reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture. This is essential for preserving natural resources and mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Enhanced Soil Health: AI-powered systems monitor soil health parameters like nutrient levels, moisture content, and compaction. This data informs soil management practices that improve fertility, reduce erosion, and enhance long-term land health. Healthy soil is the foundation of sustainable agriculture, and AI can help ensure its long-term viability.
- Climate Change Adaptation: AI empowers farmers to adapt to climate change by providing tools for predicting weather patterns, managing water resources, and developing drought-resistant crops. This is crucial for ensuring food security in a world facing increasing climate variability.

Applications of AI in Agriculture
AI is used across various aspects of agriculture, from crop management to livestock monitoring and supply chain optimization.
- Precision Agriculture:
- Variable Rate Technology (VRT): VRT systems use AI algorithms to analyze sensor data, GPS, and satellite imagery, creating detailed field maps that identify variations in soil conditions and crop needs. This enables precise application of inputs like seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides. For example, VRT can adjust the amount of fertilizer applied to different parts of a field, based on soil nutrient levels.
- Remote Sensing Technologies (RST): RST uses satellites and drones with AI-powered cameras to collect data on crop health, soil moisture, and nutrient levels, providing valuable insights for crop management. This allows farmers to monitor large areas efficiently and identify potential problems early on.
- Precision Irrigation Systems (PIS): PIS uses AI to optimize irrigation schedules based on real-time data on weather, soil moisture, and crop water requirements, conserving water and improving yields. This is particularly important in water-scarce regions.
- Smart Farming:
- Autonomous Tractors and Drones: AI powers the development of autonomous tractors and drones for tasks like planting, spraying, and harvesting, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency. These machines can operate without human intervention, freeing up farmers for other tasks.
- Smart Sensors and IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) enables the deployment of sensors throughout farms, collecting data on temperature, humidity, soil moisture, and crop growth. AI algorithms analyze this data to provide real-time insights. This creates a connected farm where data is constantly collected and analyzed to optimize operations.
- AI-Powered Decision Support Systems: These systems provide farmers with data-driven recommendations on various aspects of farm management, including crop selection, planting, irrigation, pest control, and harvesting. This helps farmers make informed decisions based on real-time data and AI analysis.
- Livestock Farming:
- Health Monitoring and Disease Detection: AI-powered systems monitor livestock health using sensors, cameras, and wearables, detecting early signs of disease and alerting farmers. This can help prevent outbreaks and improve animal welfare.
- Precision Feeding: AI algorithms analyze data on individual animals to determine their specific nutritional needs, enabling personalized feeding regimens. This optimizes animal health and productivity while reducing feed waste.
- Automated Livestock Management: AI automates tasks like milking, feeding, and cleaning, reducing labor costs and improving animal welfare. This can free up farmers’ time for other tasks and improve the efficiency of livestock operations.
- Crop and Soil Analysis:
- Image Recognition for Crop Health Assessment: AI-powered systems analyze crop images to identify signs of disease, pests, or nutrient deficiencies for early detection and intervention. This can help prevent crop losses and reduce the need for pesticides.
- AI-Powered Soil Testing: AI algorithms analyze soil samples to determine nutrient levels, pH, and other factors affecting crop growth. This helps farmers make informed decisions about fertilizer application and soil management practices.
- Yield Prediction: AI analyzes historical data, weather patterns, and soil conditions to predict crop yields. This helps farmers plan their planting and harvesting schedules and optimize resource allocation.
- Pest and Disease Management:
- Early Detection and Identification: AI-powered systems detect and identify pests and diseases early, even before visible symptoms appear. This allows for timely intervention and minimizes crop damage.
- Targeted Pesticide Application: AI-enabled drones and robots apply pesticides precisely to affected areas, reducing overall pesticide use. This minimizes environmental impact and protects beneficial insects.
- Disease Prediction and Prevention: AI algorithms analyze data to predict potential disease outbreaks, allowing for preventive measures. This can help reduce crop losses and the need for chemical treatments.
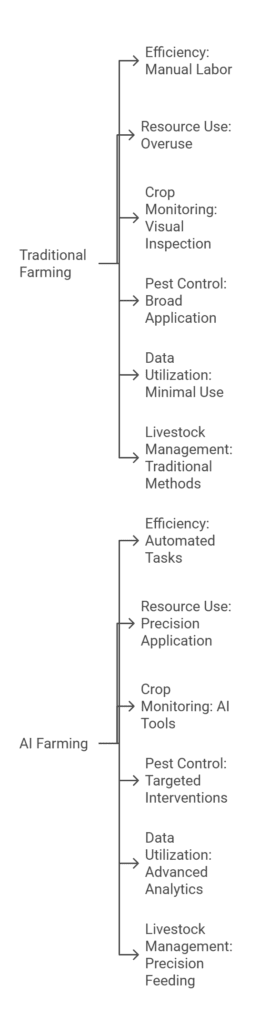
AI and Food Security
AI enhances food security on a global scale by:
- Increasing productivity through precision farming techniques
- Reducing waste by predicting and preventing crop losses
- Optimizing resource use for sustainable production
- Improving food distribution and storage efficiency
AI for Smallholder Farmers
AI empowers smallholder farmers by:
- Providing real-time information on weather patterns, soil conditions, and crop health
- Connecting farmers with buyers and markets
- Making AI technologies more affordable and accessible
AI and Agricultural Education
AI is transforming agricultural education through:
- AI-powered educational platforms providing personalized learning experiences
- Interactive simulations and learning games
- Performance analysis and feedback for students
Case Studies: Real-World Impact of AI in Agriculture
1. Intellias’ Smart Agricultural Solutions
- Crop Management Software: Developed to help farmers comply with EU environmental standards, this platform offers tools like soil health management and risk assessment for sustainable practices.
- Comprehensive Farm Management: This solution integrates weather analysis, disease monitoring, satellite imagery, and operational planning, demonstrating the breadth of AI’s utility in modern agriculture.
2. John Deere’s Autonomous Tractors
John Deere’s AI-enabled 8R autonomous tractors exemplify how automation streamlines farming tasks like tilling and planting. These machines enhance efficiency while reducing human labor dependency.
3. Precision Irrigation in California
A cloud-based vine stress monitoring system boosted grape yields by 26% and cut water consumption by 16%. This case highlights how AI-driven irrigation optimizes resource use for higher profitability.
4. Blue River Technology’s Innovations
Acquired by John Deere, Blue River Technology specializes in precision weed control robotics, drastically minimizing herbicide use, and fostering eco-friendly farming practices.
5. Jivabhumi’s Marketplace Empowerment
This AI-powered platform connects small-scale farmers to buyers, improving market access and optimizing supply chains. Jivabhumi is a testament to AI’s potential for empowering marginalized farming communities.
The Future of AI in Agriculture: A Glimpse into Tomorrow’s Farms
The future of AI in agriculture is promising, with ongoing innovation leading to more sophisticated solutions:
- Increased Integration: AI will increasingly integrate with other technologies like blockchain, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to create interconnected agricultural ecosystems. This will enable seamless data sharing and automation across all aspects of farming.
- New AI-Powered Tools: Researchers are developing new tools, including systems for predicting crop yields with even greater accuracy, optimizing fertilizer use based on real-time plant needs, and detecting plant diseases at the molecular level. These advancements will further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of agriculture.
- Greater Adoption by Small-Scale Farmers: As AI technologies become more affordable and accessible, they will be adopted by a wider range of farmers, including those in developing countries. This will help to promote food security and economic development on a global scale.
Challenges and Considerations for AI in Agriculture:
While the potential of AI in agriculture is vast, there are challenges to address:
Challenges and Considerations for AI Adoption
While the transformative potential of AI in agriculture is undeniable, several challenges persist:
1. Financial Barriers
High upfront equipment, software, and training costs make AI adoption daunting, particularly for small and medium-scale farmers. Policies like subsidies or tax incentives could help alleviate these financial hurdles.
2. Technical Knowledge Gap
The lack of expertise in operating AI systems creates resistance among farmers. Bridging this gap requires accessible training programs, user-friendly interfaces, and partnerships with agricultural institutions.
3. Data Privacy Concerns
Agricultural data, including soil health and livestock performance, is sensitive. Establishing robust data governance frameworks is essential to maintain trust and protect stakeholders’ interests.
4. Ethical Implications
AI could displace agricultural laborers, raising concerns about employment. Additionally, the concentration of power within large technology companies must be addressed to ensure inclusivity and equity in AI benefits.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges:
- Encourage collaboration among governments, tech companies, and farmers.
- Invest in rural broadband for better internet access.
- Promote public-private partnerships to develop affordable AI solutions.
Conclusion: AI for a Sustainable and Abundant Future
AI is revolutionizing agriculture, offering a powerful way to optimize operations, increase productivity, and promote sustainability. AI can help create a more sustainable, efficient, and equitable global food system, by empowering farmers with data-driven insights, automating tasks, and optimizing resource use. As the world’s population grows and climate change intensifies, AI in agriculture offers hope for meeting our food needs and ensuring a prosperous future for all.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered professional agricultural or technological advice.
.
